Introduction
A rational number is a type of number which is explained in brief in the chapter
What are the Types of Numbers Used in Maths? also.
This chapter explains all the basics of rational numbers with its definition, examples, positive and negative
rational numbers, equivalent rational numbers and how to compare two rational numbers with opposite and same
signs.
You will learn how to represent a rational number on a number line with steps to draw.
There are numbers of worksheets available at the end of this chapter to practice rational numbers
problems.
What is rational number?
A number which can be written in the form of pq, where p and q are integers and q ≠ 0.
12 , 67 , 910 and 310
Rational numbers are also written in terminating decimal or non terminating repeating decimal forms.
3.45 = 345100
0.2 = 15
11.575 = 115751000
19 = 0.11111……
13 = 0.33333……
23 = 0.66666……
Even 0 is also a rational number because 0 can be written as 0 = 0 1
Rational numbers can be positive and negative also.
1. Positive rational numbers
When both numerator and denominator of a rational number are positive integers, it is called positive rational number.
37 , 45 and 68
2. Negative rational numbers
When the numerator is a negative integer and denominator is a positive integer, it is called a negative rational number.
– 57 , – 43 and – 12
0 is neither a positive nor negative rational number.
Standard form
A rational number is said to be in its standard form if its numerator and denominator do not have any common factors other than 1 and its denominator must be a positive integer.
Conversion to standard form
If a rational number is not in the standard form then it can be converted into its standard form by taking HCF of its numerator and denominator. The numerator and denominator are divided by HCF together. The rational number obtained after the division will be its standard form.
Convert 1220 into its standard form
HCF of numerator 12 and denominator 20 is 4
Divide both 12 and 20 by 4
12 ÷ 420 ÷ 4 =
35
Convert 14– 18 into its standard
form
HCF of numerator 14 and denominator 18 is 2
Divide both 14 and – 18 by – 2
14 ÷ – 2– 18 ÷ – 2 =
– 79
Equivalent rational number
When numerator and denominator of any rational number is multiplied by any non zero number, the resulting rational number is equivalent to the original rational number.
46 is equivalent to
23
because, 23 ×
22 =
46
Comparison of rational numbers
Like integers, the two rational numbers can also be compared to find out which is the largest or the smallest rational number. But the method to find out the largest or the smallest depends upon the sign of the rational number.
Rational numbers of opposite sign
When two rational numbers are of opposite sign then they are compared same like integers. Positive integers are always greater than the negative integers, the same rule applies for rational numbers of opposite sign also. So, positive rational numbers are always greater than negative rational numbers also.
Which is greater 23 or
– 45?
Since, both rational numbers have opposite signs, so the positive rational will be grater than
the negative rational number
∴ 23 >
– 45
Rational numbers of same sign
Two rational numbers are of same sign means both can be of negative signs or positive signs. To compare such numbers fist find the LCM of denominators of both numbers. Then multiply the both rational numbers with a number so that the values of the denominators become equal to the LCM. Now the numerators of both given numbers can be compared because same they have same denominators. The rational number with the greater numerator will also be greater than the other rational number.
Which is greater 27 or
45?
Since, both rational numbers have same signs, so find the LCM of denominators 7 and 5, which will be 35
Now, multiply 27 and
45 with the number so that denominators
of both become equal to LCM 35.
23 ×
55 =
1035
45 ×
77 =
2835
Compare the numerators 28 and 35
28 > 10
∴ 2835 >
1035
or 45 >
27
Which is smaller – 34 or
– 59?
Both rational numbers have same signs, so find the LCM of denominators 4 and 9, which will be 36
Now, multiply – 34 and
– 59 with the number so that denominators
of both become equal to LCM 36.
– 34 ×
99 =
– 2736
– 59 ×
44 =
– 2036
Compare the numerators – 27 and – 20
– 27 < – 20
∴ – 2736 <
– 2036
or – 34 <
– 59
Representation on number line
Rational numbers can be represented on the number line same like integers.
The following steps are taken to represent them on the number line.
Step 1
Draw a number line with positive numbers on the right hand side and negative number on the left hand side
of 0.
Step 2
Divide 0 and 1 on the number line into n equal points,
where n is the value of the denominator and write the points as
1n ,
2n ,
3n ,
4n etc.
Mark the point on the number line which matches to the given rational number.
Example 1: Represent 37 on number
line.
Step 1
Draw a number line with positive and negative numbers on the right and left hand sides of 0
respectively.
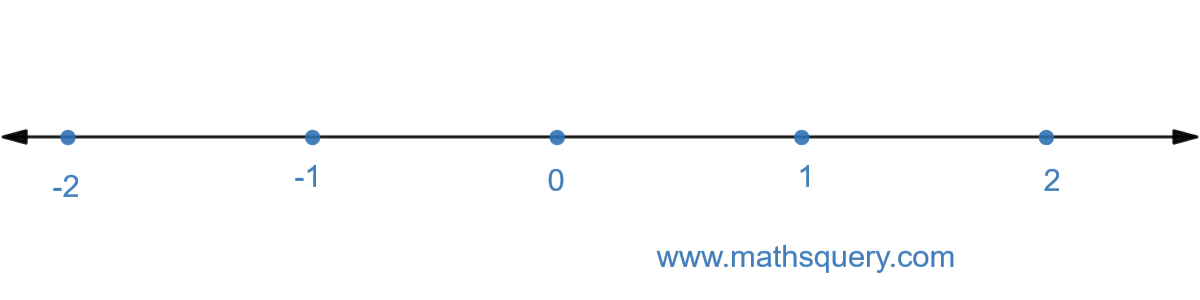
Step 2
Here, denominator is 7, ∴ n = 7.
So, divide 0 and 1 on the number line into 7 equal points and mark each point as
07 ,
17 ,
27 ,
37 ,
47 ,
57 ,
67 and
77
Length of each part between two adjacent points is
17.
Now, start from 0 and mark the point
37 on the number line with A.

So, 37 is represented on the number
line with point A
Example 2: Represent 74 on number
line.
Step 1
Draw the number line.
Step 2
Here, denominator is 4, so n = 4.
Divide 0 and 1 into 4 equal points
Because the value of denominator is less than value of numerator, so do the same from 1 to 2, i.e. divide them
into 4 equal parts also.
Length of each part between two adjacent points is
14.
Mark the point
74 on the number line with A.
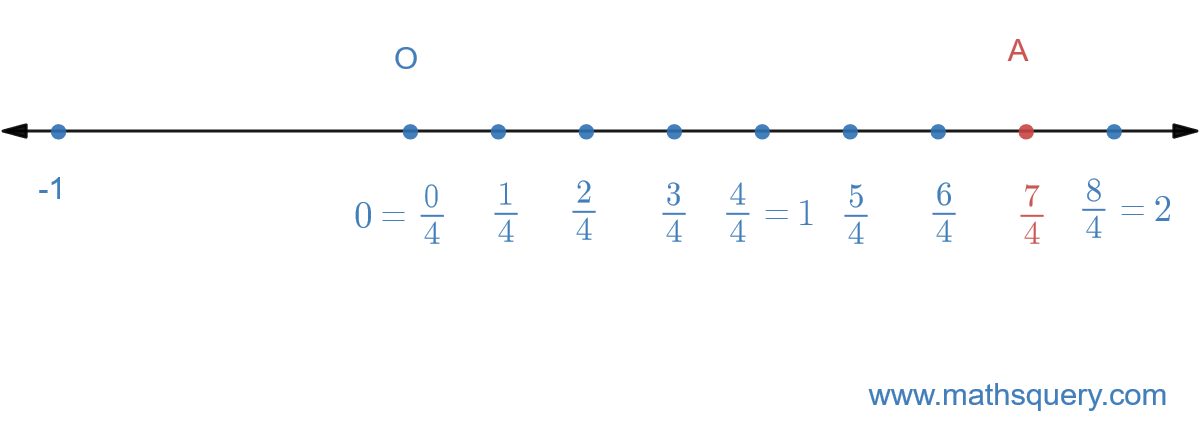
So, 74 is represented on the number
line with point A.
Example 3: Represent 27 on number
line.
To represent 27
on number line, we divide 0 to 1 into 7 equal parts.
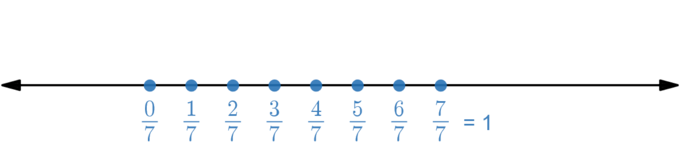
Match Columns Worksheet
| Type: | Matching |
| Count: | 1 |
| Rational number | Equivalent rational number | ||
| 1) | 45 | a) | 927 |
| 2) | - 67 | b) | - 3528 |
| 3) | 13 | c) | - 7284 |
| 4) | - 54 | d) | 91104 |
| 5) | 78 | e) | 1620 |
Compare Columns Worksheet
| Type: | Comparing |
| Count: | 1 |
Put >, < or = in the boxes.
| 1) | 27 | 57 | |
| 2) | 125 | - 125 | |
| 3) | - 113 | 103 | |
| 4) | 12 | 15 | |
| 5) | - 43 | - 53 | |
| 6) | - 12 | - 13 | |
| 7) | - 12 | - 918 | |
| 8) | - 45 | - 43 | |
| 9) | 32 | 23 | |
| 10) | 45 | 2835 |
Solve Questions Worksheets
| Type: | Solve Questions |
| Count: | 3 |
Arrange the following rational numbers into ascending order.
- 13 , 23 , - 13 , - 43
- 25 , 105 , - 115 , - 95
- 76 , - 86 , 46 , - 106
- - 12 , 12 , - 52 , - 92
- 87 , - 87 , - 37 , 37
Arrange the following rational numbers into descending order.
- 24 , 14 , - 14 , - 74
- 87 , - 47 , - 87 , - 97
- 1311 , - 1411 , 711 , 911
- 89 , - 119 , - 19 , 79
- 43 , 03 , - 13 , - 113
Draw a number line and represent the following rational numbers on the number line.
- 54
- 45
- 32
- 27
- 23
















