Introduction
In the chapter Point, Line, Ray, Line Segment and Plane we learnt about the basic geometrical concepts of rays. The inclination of these rays to each other leads to the formation of an angle. The word “angle” originates from the latin word which is “angulus”, which means in latin as corner.
In daily life we can see an example of angle formation when a ladder is leaned against a wall. In such scenario of leaned ladder against the wall, the angle is formed at top of the ladder where ladder and wall meet at a point and the second angle is formed where ladder and floor meet at a point.
Let’s take a deep look at the basics of angle, its measurements and various types.
What is an Angle?
A figure formed by joining two different rays starting from the same fixed initial point is called an angle.

In the given figure, this figure is made up of two rays
OA
and
OB
.
The
common end point of two rays is called the vertex of the angle.
So, O is the vertex of angle AOB.
The rays
OA
and
OB
are called the arms or sides of angle AOB.
An angle is denoted by the symbol ∠.
Only capital letters of English alphabets are used to name an angle. Name of angles can be written using
three
or one alphabet.
Thus, we can write the above angle in figure as ∠AOB or ∠BOA or ∠O.
We can see from the naming that vertex is always kept at the centre when written using three alphabets and
only
vertex when written as a single alphabet.
Measurement of angle
The unit of measuring an angle is degree.
The word degree originates from the Latin word “gradius” which means “step”. It refers to a stage in an
ascending or
descending order.
The symbol used for degree is “°”. It is inserted on the right top of the numeral.
for example, 90 degrees = 90°
Types of angle
1. Acute angle
An angle which is less than 90°, is called acute angle.

2. Right angle
An angle which is equal to 90°, is called right angle.

3. Obtuse angle
An angle which is greater than 90° and less than 180° is called obtuse angle.

4. Straight angle
An angle which is equal to 180°, is called straight angle or straight line angle.

5. Reflex angle
An angle which measure greater than 180° but less than 360° is called reflex angle.

6. Complete angle
An angle is said to be complete angle if two different rays coincide with initial point after making a complete revolution.

Here, ray
OA
and ray
OB
coincide each other after making a complete
revolution.
∠AOB = 360°
7. Zero angle
An angle is said to be zero angle if two different rays coincide without any revolution.

Here, ray
OA
and ray
OB
coincide ∠AOB
∠AOB = 0°
The acute and obtuse angles are known as oblique angles.
What are Congruent angles?
Angles having the same measure are said to be congruent angles.

What are Adjacent angles?
Two angles are said to be adjacent angles if they have common vertex, a common arm and other two arms of the angles are on the opposite sides of the common arm.

In the given figure, two angles ∠AOB and ∠BOC have a common arm OB, a common vertex O and the other two arms OA and OC lie on the opposite sides of common arm OB.
1. Complementary angles
Two angles are said to be complementary if they form adjacent angle and sum of their measure is equal to 90°

∠AOC + ∠BOC
= 45° + 45°
90°
2. Supplementary angles
Two angles are said to be supplementary angles if they form adjacent angles whose sum of their angles is equal to 180°

∠ABO + ∠CBO
=120° + 60°
180°
List of types of angles with measures
| Name of angle | Measure |
|---|---|
| Acute angle | 0° < θ < 90° |
| Right angle | θ = 90° |
| Obtuse angle | 90° < θ < 180° |
| Straight angle | θ = 180° |
| Reflex angle | 180° < θ < 360° |
| Complete angle | θ = 360° |
| Zero angle | θ = 0° |
Solved Examples
1) Classify the following as acute, obtuse, right angle, complete angle and reflex angle.
- 27°
- 110°
- 180°
- 232°
- 360°
- 180 3° 4
-
27°
As 27° lies between 0° and 90°, it is an acute angle.
-
110°
110° is an obtuse angle because it lies between 90° and 180°.
-
180°
180° is a straight angle.
-
232°
232° is a reflex angle because it lies between 180° and 360°.
-
360°
360° is a complete angle.
-
180 3° 4
180 3° 4 =180.75° lies between 180° and 360°.
2) Find the angle formed by an hour hand of a clock when it moves:
- from 3 to 6
- from 12 to 6
- from 9 to 1
- from 7 to 12
- from 2 to 9
-
from 3 to 6
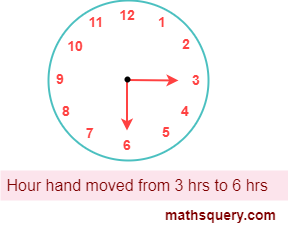
Number of hours when hour hand moves from 3 to 6 = 3 hours.
An hour hand forms 360° angle when it moves once cycle starting from 12 and ending at 12 on a clock. Or we can say, an hour hand makes 360° angle in 12 hours.
Or, angle formed in 12 hours = 360°
∴ angle formed in 1 hour = 360 12
So, angle formed in 3 hours = 360 12 × 3
= 90°
= 1 right angle
-
from 12 to 6

Number of hours when hour hand moves from 12 to 6 = 6 hours.
Angle formed by hour hand in 12 hours = 360°
angle formed in 1 hour = 360 12
So, angle formed in 6 hours = 360 12 × 6
= 180°
= a straight angle
-
from 9 to 1
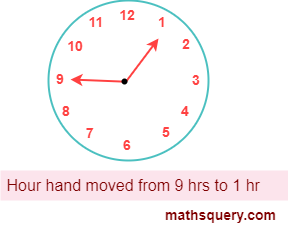
Number of hours when hour hand moves from 9 to 1 = 4 hours.
Angle formed by hour hand in 12 hours = 360°
angle formed in 1 hour = 360 12
So, angle formed in 4 hours = 360 12 × 4
= 120°
-
from 7 to 12
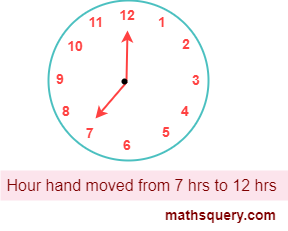
Number of hours when hour hand moves from 7 to 12 = 5 hours.
Angle formed by hour hand in 12 hours = 360°
angle formed in 1 hour = 360 12
So, angle formed in 5 hours = 360 12 × 5
= 150°
-
from 2 to 9
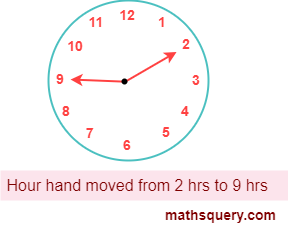
Number of hours when hour hand moves from 2 to 9 = 7 hours.
Angle formed by hour hand in 12 hours = 360°
angle formed in 1 hour = 360 12 × 6
So, angle formed in 7 hours = 360 12 × 7
= 210°
3) Out of east, west, north and south in which direction will a man be after starting a walk towards west, then taking a turn of 1 2 revolution in clockwise direction.

1 revolution = 360°
1
2
revolution =
1
2
× 360
= 180°
So, the man started walking in west direction and takes a turn of
1
2
revolution which will be 180° in clockwise direction.
From the diagram, the east direction is at 180° of west direction in clockwise.
So, the man finally will be moving towards east direction.
4) Out of east, west, north and south in which direction will a man be after starting a walk towards north, then taking a turn of 3 4 revolution in anticlockwise direction.
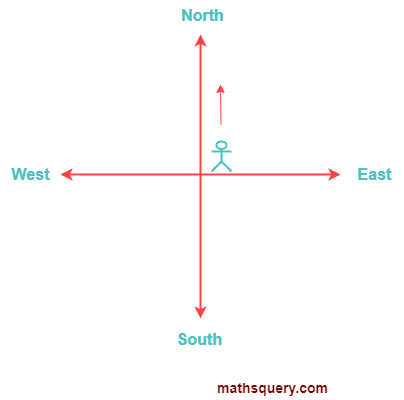
1 revolution = 360°
3
4
revolution =
3
4
× 360 = 270°
So, the man started walking in north direction and takes a turn of
3
4
revolution which will be 270° in anti clockwise direction.
From the diagram, the west direction is at 270° of north direction in anticlockwise.
So, the man finally will be moving towards west direction.
Fill in Blanks Worksheet
| Type: | Blanks |
| Count: | 1 |
- The measure of one complete angle is equal to four ___________ angles.
- An angle of 180° measure is called ___________.
- The common initial point of two rays is called as ___________.
- An angle whose measure is greater than that of the right angle but less than 180° is ___________.
- The two intersecting rays at a point form an angle, the two rays are called as ___________ of the angle.
- The measure of 2 right angles is ___________.
- The sum of two angles is 90°, then each of them is ___________ angle.
- At 7 o'clock, the angle formed between minute hand and hour hand is a ___________ angle.
- At 12 o'clock, the angle formed between minute hand and hour hand is ___________.
- 1 2 of straight angle is equal to ___________.
Geometry Worksheets
| Type: | Geometry |
| Count: | 2 |
Classify the following angles into acute angle, obtuse angle, straight angle, right angle and complete angle.
- 120°
- 45°
- 130°
- 360°
- 90°
- 91°
- 140°
- 240°
- 170°
- 180°
Write the name of angle for each of the following figure.
| 1. |

|
___________ |
| 2. |

|
___________ |
| 3. |

|
___________ |
| 4. |

|
___________ |
| 5. |

|
___________ |
Multiple Choice Questions Worksheet
| Type: | MCQ |
| Count: | 1 |
- 360°
- 270°
- 180°
- 90°
- 90°
- 180°
- 360°
- 270°
- 180°
- 90°
- 270°
- 360°
- 90°
- 180°
- 0°
- 270°
- obtuse angle
- right angle
- straight angle
- reflex angle
- 90°
- 180°
- 270°
- 360°
- 1 right angle and 1 obtuse angle
- 1 straight angle and 1 acute angle
- both obtuse angle
- both acute angles
- 180°
- 90°
- 270°
- 360°
- acute
- obtuse
- right
- straight
- 1 right angle
- 2 right angles
- 3 right angles
- 4 right angles















