Relationship between Lines and Angles
We have learnt the basics of angles, their measures and various types of angles in the
chapter Angle, its Measures and Types of Angle.
As we have seen, angles are formed only when two lines intersect at some point. So, there are many more case
where different types of angles are defined
when lines intersect each other.
Such angles are formed by a transversal line when it intersects two or more parallel or non parallel lines.
Vertically Opposite angles
When two straight lines intersect each other, they form four angles at the point of intersection. Out of four angles the two angles which are directly opposite to each other are called vertically opposite angles. These two vertically opposite angles are always equal.

Here, in the above diagram, we can see ∠AOD, ∠BOC, ∠AOC and ∠BOD are the four angles formed at point O when two lines AB and CD intersect at point O.
The angles ∠AOD and ∠BOC are directly opposite to each other, therefore they are called vertically opposite angles and ∠AOD = ∠BOC
Similarly, the angles ∠AOC and ∠BOD are also directly opposite to each other, therefore they
are also called vertically opposite angles
and ∠AOC = ∠BOD
Moreover, the sum of each pair of adjacent angles is alway equal to 180°.
∠AOC + ∠BOC = 180°
∠AOC + ∠AOD = 180°
∠BOC + ∠BOD = 180°
∠AOD + ∠BOD = 180°
Exterior angles
Exterior angles are formed at points on the exterior sides of the two lines where a transversal line intersects
these two lines.
Let’s understand it by an example.

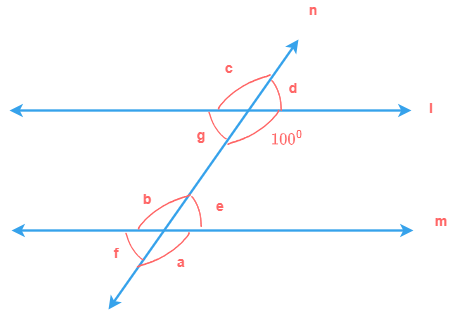
∠1, ∠2, ∠7 and ∠8 are formed at points A and B on the exterior sides of two non parallel lines l and m respectively, when a transversal line n cuts through them. Therefore, ∠1, ∠2, ∠7 and ∠8 are called exterior angles.
Interior angles
Interior angles are formed at points on the interior sides of the two lines where a transversal line intersects
these two lines.
Let’s understand it by an example.

∠3, ∠4, ∠5 and ∠6 are formed at points A and B on the interior sides of two non parallel lines l and m respectively, when a transversal line n cuts through them. Therefore, ∠3, ∠4, ∠5 and ∠6 are called interior angles.
Alternate angles
Alternate angles again are formed when a transversal line cuts through two parallel or non parallel lines.
These angles are a pair of angles which can exist on the interior or exterior sides of the two lines.
We can understand it more precisely with the following example.

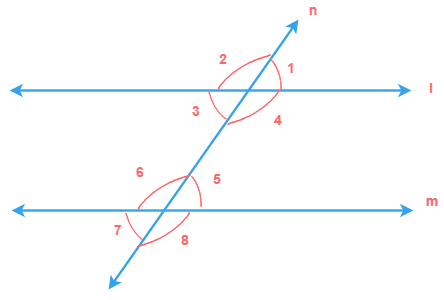
Here, a transversal line n cuts thru two lines l and m and forms total of eight angles at points A and B which are:
∠1, ∠2, ∠3, ∠4, ∠5, ∠6, ∠7 and ∠8.
If we select the pairs of angles in the following way, then these pairs are the alternate angles.
∠1 and ∠7
∠2 and ∠8
∠3 and ∠6
∠4 and ∠5
Depending upon where the pair exists on the two lines l and m we can name them alternate interior angles and
alternate exterior angles.
e.g. here, the pairs of alternate angles ∠1 and ∠7, ∠2 and ∠8 lie
outside the lines
i.e. exterior sides of the two lines, such type of alternate angles are called alternate exterior
angles.
Similarly, the pairs of alternate angles ∠3 and ∠6, ∠4 and ∠5 lie inside the lines i.e. interior sides of the two lines, such type of alternate angles are called alternate interior angles.
The pair of alternate angles formed with parallel lines are always equal.
In the above example, lines l and m are parallel lines. So, we can see that the following alternate angles pairs
are equal
∠1 = ∠7
∠2 = ∠8
∠3 = ∠6
∠4 = ∠5
Corresponding angles
A pair of angles is called corresponding angles in which one arm of both angles is on the same side of
transversal and their other arms are directed in the same sense.
If lines l and m are parallel, then pairs of corresponding angles are equal.
Let’s understand it with the following example.

So, from the above diagram, the following pair of angles are corresponding angles that are formed on two parallel lines l and m.
∠1 and ∠6
∠2 and ∠5
∠3 and ∠7
∠4 and ∠8
As said above, these pairs of angles, also called as corresponding angles, are always equal.
Therefore, we can write them as:
∠1 = ∠6
∠2 = ∠5
∠3 = ∠7
∠4 = ∠8
More, in parallel lines l and m, sum of interior angles of the same side of transversal is 180° i.e.
∠4 + ∠6 = 180°
∠3 + ∠5 = 180°
Linear pair of angles
When sum of two adjacent angles is 180°, they are called linear pair of angles.
Or, we can say when supplementary angles formed on a straight line, those angles are called a linear pair
of
angles.

In the above diagram, ∠ABO + ∠CBO = 180°, therefore, they form a linear pair of angles.
Solved Examples
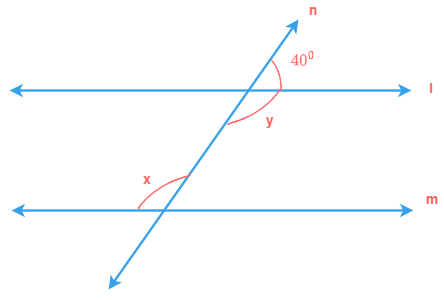
1) Find the value of x.
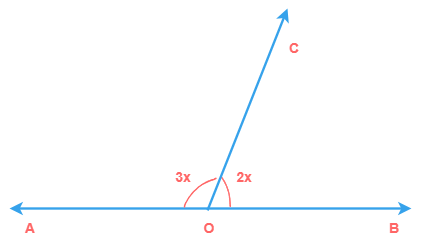
Solution
Since, ∠AOC + ∠BOC = 180° (linear pair)
3x + 2x = 180°
5x = 180°
x = 36°
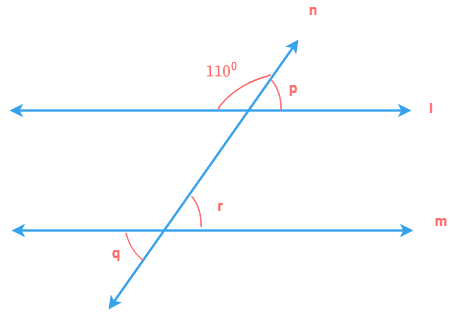
2) Find the ∠POR.
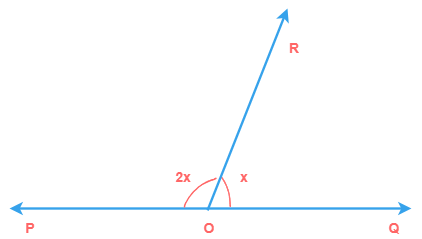
Solution
∠POR + ∠QOR = 180° (linear pair)
2x + x = 180°
3x = 180°
x = 60°
∠POR = 2x
∠POR = 2 × 60
∠POR = 120°
3) Find the value of x.
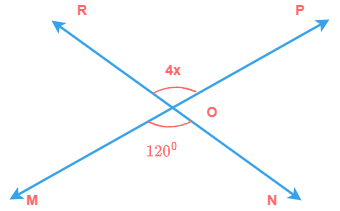
Solution
Since, ∠POR & ∠MON are vertically opposite angles
∴ ∠POR = ∠MON
4x = 120°
x = 30°
4) Find the value ∠1, ∠2 and ∠3, if ∠4 = 30°.
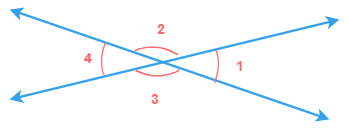
Solution
∠1 & ∠4 are vertically opposite angles
∴ ∠1 = ∠4
∴ ∠1 = 30°
Also, ∠1 + ∠2 = 180°
30° + ∠2 = 180°
∠2 = 180° - 30°
∠2 = 150°
Also, ∠2 = ∠3 because vertically opposite angles
∴ ∠3 = 150°
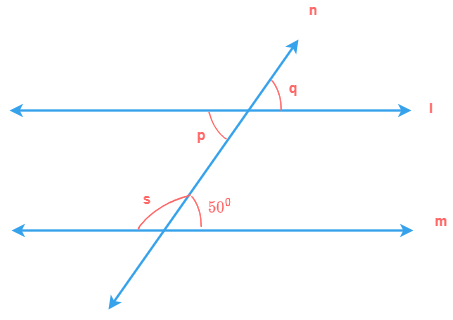
5) If p || q and r is transversal. Find the value ∠1, ∠2 and ∠3, if ∠4 = 110°.
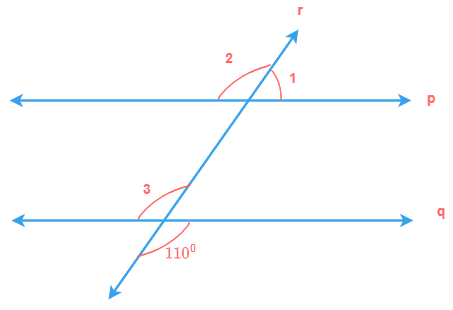
Solution
∠3 & ∠4 are vertically opposite angles
∴ ∠3 = 110°
∠2 & ∠3 are corresponding angles
∴ ∠2 = ∠3
∴∠2 = 110°
Also, ∠1 + ∠2 = 180° (∵ linear pair)
∠1 + 110° = 180°
∠1 = 180° - 110°
∠1 = 70°
6) If p || q, ∠1 and ∠2 and are in the ratio of 2 : 3. Find angles ∠3, ∠4, ∠5, ∠6, ∠7 and ∠8.
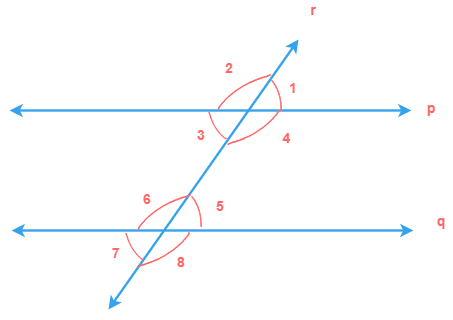
Solution
∠1 : ∠2 = 2 : 3
Also ∠1 + ∠2 = 180° [because ∠1 and ∠2 are linear pair]
2x + 3x = 180°
5x = 180°
x = 36°
∠1 = 2x = 2 × 36° = 72°
∠2 = 3x = 3 × 36° = 108°
∠1 = ∠3 (because vertically opposite angles)
∴ ∠3 = 72°
Also, ∠2 = ∠4 (because vertically opposite angles)
∠4 = 108°
Also, ∠1 = ∠5 (because corresponding angles)
∠5 = 72°
Also, ∠2 = ∠6 (because corresponding angles)
∠6 = 108°
Also, ∠6 = ∠8 (because vertically opposite angles)
∠8 = 108°
∠5 = ∠7 (because vertically opposite angles)
∠7 = 72°
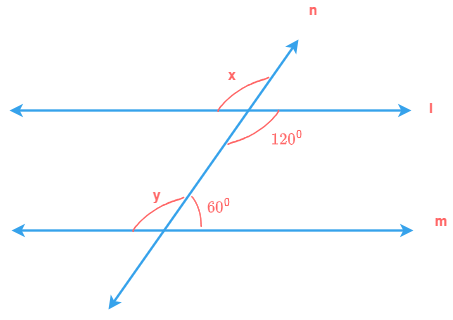
7) If AB || CD, find the values of x and y.
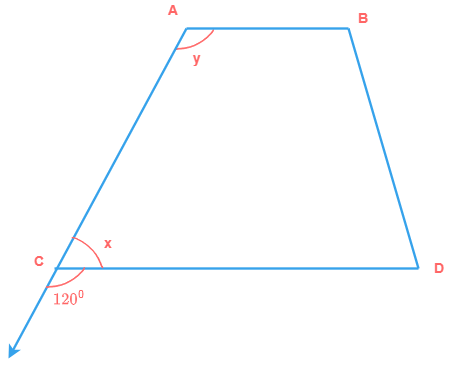
Solution
Since, x and 120° form a linear pair.
∴ ∠x + 120° = 180°
∠x = 180° - 120°
∠x = 60°
Also, AB || CD
∴ ∠ACD + ∠CAB = 180°
Because sum of interior angles on the same side of a transversal is 180°
60° + ∠y = 180°
∠y = 180° - 60°
∠y = 120°
8) In the figure, p || q, r || s and ∠1 = 105°. Find the other angles.
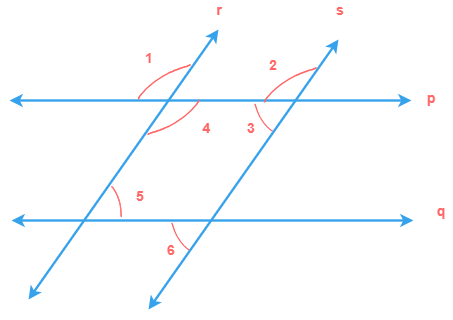
Solution
Since, ∠1 and ∠4 are vertically opposite angles.
∴ ∠1 = ∠4
∠4 = 105°
Since, r || s and p is transversal to r and s.
∠1 and ∠2 form corresponding angles.
∴ ∠1 = ∠2
∠2 = 105°
Also, ∠2 + ∠3 = 180°
105° + ∠3 = 180°
∠3 = 180° - 105°
∠3 = 75°
Now p || q and r is transversal to p and q.
∠4 + ∠5 = 180° (because sum of interior angles on the same side of transversal is
180°)
∠4 + ∠5 = 180°
105° + ∠5 = 180°
∠5 = 180° - 105°
∠5 = 75°
Since p || q and s is also transversal to p and q.
∴ ∠3 and ∠6 are corresponding angles.
∴ ∠3 = ∠6
∠6 = 75°
9) In the following figure FG || DE, ∠B = 30° and ∠C = 50°. Find values of x, y and z.
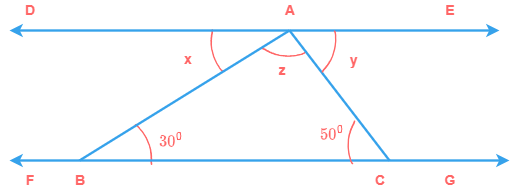
Solution
Since, FG || DE and AB is transversal to FG and DE.
∠x = 30°
Also, FG || DE and AC is transversal to FG and DE.
∴ 50° and y are alternate interior angles.
∠y = 50°
Also, ∠x + ∠y + ∠z = 180° (because x, y and z form linear pair)
30° + 50° + ∠z = 180°
80° + ∠z = 180°
∠z = 180° - 80°
∠z = 100°
10) In the given figure PQ || SR and PS || QR. Find the values of x, y and z.
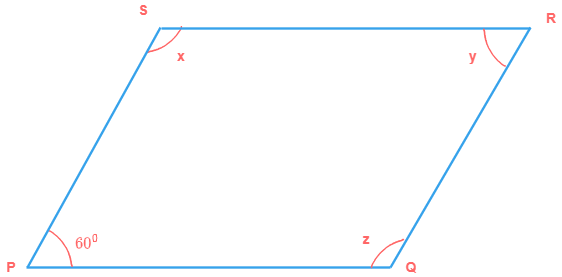
Solution
Since, PQ || SR and PS is transversal to PQ and SR.
∠S and ∠P are co-interior angles
∴ ∠x + 60° = 180° (because co-interior angles are supplementary)
∠x = 180° - 60°
∠x = 120°
Also, PS || QR and PQ is transversal to PS and QR.
∠P and ∠Q are co-interior angles
∴ 60° + ∠z = 180° (because co-interior angles are supplementary)
∠z = 180° - 60°
∠z = 120°
Similarly, PS || QR and SR is transversal to PS and QR.
∠S and ∠R are co-interior angles
∴ ∠x + ∠y = 180° (because co-interior angles are supplementary)
120° + ∠y = 180°
∠y = 180° - 120°
∠y = 60°
Fill in Blanks Worksheet
| Type: | Blanks |
| Count: | 1 |
By observing the following figure, fill the blanks in.
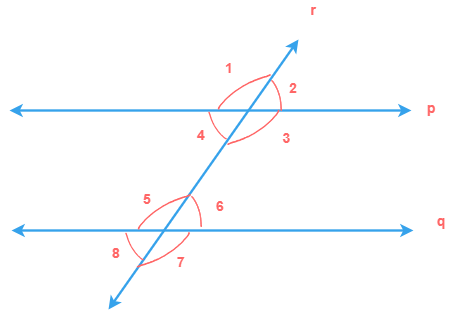
- If p || q and ∠1 = ∠5, then these are ___________ angles.
- If p || q then ∠5 + ∠6 = ___________.
- If ∠4 = ∠6, then line p must be ___________ to line q.
- If p || q and ∠1 = ∠3, then these are ___________ angles.
- If p || q and ∠2 = ∠8, then these are ___________ angles.
Write True or False Worksheet
| Type: | True False |
| Count: | 1 |
| S.N. | Statement | ✓ or ✕ |
|---|---|---|
| 1) | If two lines intersect in the same plane then these lines must be parallel. | |
| 2) | If a line intersects two lines then the line is parallel to the two lines. | |
| 3) | When two straight lines intersect each other at a point then the vertically opposite angles formed at the point of intersection are unequal. | |
| 4) | The sum of two adjacent angles on a same line is 180°. | |
| 5) | The distance between two parallel lines remains the same. | |
| 6) | If two parallel lines are cut by a transversal line then their corresponding angles must be equal. | |
| 7) | The interior alternate angles are equal, if non parallel lines are cut by a transversal. | |
| 8) | If line m is parallel to n and n is parallel to p then m is parallel to p. | |
| 9) | The distance between two intersecting lines is zero. | |
| 10) | When a transversal cuts two lines such that a pair of alternate exterior angles are unequal then the two lines must be non parallel to each other. |
Match Columns Worksheet
| Type: | Matching |
| Count: | 1 |
| 1) | alternate interior angles | a) | ∠2, ∠4 |
| 2) | alternate exterior angles | b) | ∠1, ∠5 |
| 3) | vertically opposite angles | c) | ∠3, ∠5 |
| 4) | corresponding angles | d) | ∠7, ∠8 |
| 5) | linear pair | e) | ∠1, ∠7 |
Geometry Worksheet
| Type: | Geometry |
| Count: | 1 |
In the following figures, find the missing values.
Multiple Choice Questions Worksheet
| Type: | MCQ |
| Count: | 1 |

- p and q
- p and r
- q and r
- q and s
- ∠3 and ∠7
- ∠5 and ∠7
- ∠1 and ∠2
- ∠1 and ∠3
- ∠1 and ∠2
- ∠2 and ∠3
- ∠5 and ∠7
- ∠3 and ∠4
- ∠2 and ∠11
- ∠2 and ∠4
- ∠2 and ∠3
- ∠6 and ∠11
- ∠1 and ∠9
- ∠1 and ∠5
- ∠6 and ∠7
- ∠3 and ∠4
- ∠5 and ∠11
- ∠1 and ∠2
- ∠5 and ∠8
- ∠5 and ∠7
- 360°
- 180°
- 270°
- 90°
- 90°
- 180°
- 270°
- 360°
- 270°
- 360°
- 90°
- 180°
- corresponding angles
- vertically opposite angles
- alternate exterior angles
- alternate interior angles